In the intricate web of the digital world, the security of personal data is a paramount concern. This section delves into the strategies employed by malicious actors to deceive users into divulging sensitive information. By understanding these tactics, individuals can equip themselves with the necessary tools to protect their digital footprints.
Deceptive Practices are a common method used to trick unsuspecting users. These involve sophisticated attempts to mimic legitimate entities, often through emails or messages that appear genuine. The goal is to induce recipients to click on links or provide confidential details, which can then be exploited for nefarious purposes.
Awareness is the first step towards defense. Recognizing the signs of these deceptive communications is crucial. Features such as unusual requests for personal information, unexpected attachments, or links that do not match the official website of the purported sender can all be red flags. It is essential to approach such communications with a critical eye and verify the authenticity of the sender through independent means.
Implementing robust Security Measures is another vital component of protection. This includes using strong, unique passwords for different accounts, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping software updated to defend against the latest threats. Additionally, educating oneself about the evolving landscape of digital security can significantly enhance one’s ability to navigate the online world safely.
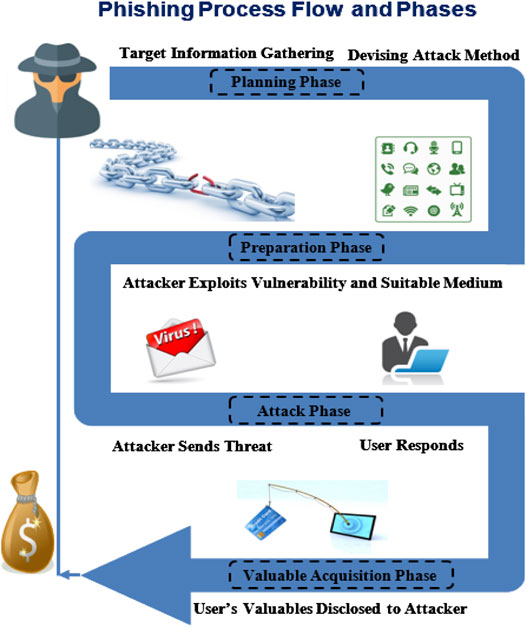
Understanding Phishing Scams
In this section, we delve into the intricate details of deceptive emails designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information. These messages, crafted to appear legitimate, often originate from seemingly trustworthy sources, making them particularly dangerous.
The structure of a deceptive email typically involves several key components. Firstly, the sender’s address is often spoofed to resemble a known entity, such as a bank or a popular service provider. This initial deception is crucial in establishing a false sense of security.
Secondly, the content of the email is meticulously designed to evoke a sense of urgency or fear. Common tactics include warnings of account closures, security breaches, or missed payments. The goal is to prompt immediate action from the recipient, often in the form of clicking on a link or providing personal details directly within the email.
Embedded within these emails are links that, when clicked, lead to fraudulent websites. These sites are replicas of the real ones, designed to capture login credentials, financial information, or other sensitive data. The URLs of these fake sites often differ from the authentic ones by only a few characters, making them difficult to detect without careful scrutiny.
Lastly, the email may include attachments that, when opened, can deploy malware or viruses onto the recipient’s device. This further enhances the potential damage from such a deceptive message, as it not only seeks to extract information but also to compromise the security of the device itself.
Understanding these elements is essential in recognizing and mitigating the risks associated with deceptive emails. By being aware of these tactics, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves against such threats.
The Anatomy of a Phishing Email
This section delves into the structure and components of deceptive emails designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information. Understanding these elements can significantly enhance your ability to identify and thwart such attempts.
Deceptive emails, often crafted to appear as if they are from legitimate sources, use various strategies to manipulate recipients. Below is a table outlining common tactics employed in these emails:
| Tactic | Description |
|---|---|
| Impersonation | The email pretends to be from a known company or individual, often using similar logos and signatures to appear authentic. |
| Urgency | The message creates a sense of urgency, prompting the recipient to act quickly without proper verification, often due to a threat of account closure or similar consequences. |
| Request for Sensitive Information | The email requests personal details such as passwords, opt out white pages account numbers, or other sensitive information, often under the guise of security updates or verification processes. |
| Embedded Links | Links within the email direct to fake websites that closely resemble legitimate ones, designed to capture information entered by the user. |
| Attachments | Attachments may contain malware that can infect the recipient’s device upon opening, potentially leading to data theft or system compromise. |
By familiarizing yourself with these tactics, you can better protect yourself from falling victim to these deceptive practices. Always verify the authenticity of emails and be cautious when providing personal information online.
Common Social Engineering Tactics
This section delves into the various strategies employed by malicious actors to manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise their security. Unlike direct hacking methods, these tactics rely heavily on psychological manipulation to exploit human vulnerabilities.
One prevalent tactic is the use of deceptive communication, where attackers pose as trustworthy entities to gain the victim’s confidence. This often involves impersonating a known contact or a reputable organization to lower the victim’s guard. The goal is to create a false sense of security, making the target more likely to comply with requests for information or actions that they would otherwise be cautious about.
Another common approach is the exploitation of urgency. Attackers frequently create scenarios that require immediate action, such as threats of account closure or warnings of unauthorized access. The heightened sense of urgency can cloud judgment, leading individuals to act hastily without proper verification of the situation.
Manipulation of authority is also a frequently used tactic. By impersonating a figure of authority, such as a government official or a high-ranking company executive, attackers can exert pressure on their targets. This psychological leverage can compel individuals to comply with requests that they might question under normal circumstances.
Lastly, the tactic of appealing to altruism is employed when attackers request help or information under the guise of assisting others. This can involve posing as a charity or as an individual in need, exploiting the victim’s desire to be helpful and supportive. Such appeals can be particularly effective as they play on the victim’s empathy and willingness to assist.
Understanding these tactics is crucial for developing effective defenses against them. Awareness and vigilance are key components in protecting oneself from falling victim to these manipulative strategies.
Recognizing Suspicious URLs
In this section, we delve into the critical skill of identifying potentially harmful web addresses. Understanding how to discern safe links from dangerous ones is essential for safeguarding your digital interactions and personal data.
URLs, or Uniform Resource Locators, are the pathways to websites and resources on the internet. However, not all URLs lead to reputable destinations. Some are crafted with malicious intent, aiming to deceive users into visiting sites that can compromise their security and privacy. Here, we will explore the characteristics of suspicious URLs and provide practical tips to help you navigate the web safely.
| Characteristic | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Misspelled Domain Names | Malicious URLs often use slight variations of well-known domain names, hoping to trick users into thinking they are visiting a legitimate site. | Instead of www.example.com, you might see www.examp1e.com (where ‘1’ replaces ‘l’). |
| Unusual Top-Level Domains | Legitimate businesses typically use common top-level domains like .com, .net, or .org. Unusual TLDs can be a red flag. | www.example.xyz might be less trustworthy than www.example.com. |
| Long, Complex URLs | URLs that are excessively long and contain numerous subdomains or parameters can indicate attempts to hide malicious content. | www.example.com/secure/login?token=1234567890&redirect=fake.site |
| HTTPS Absence | While not definitive, the absence of HTTPS (indicated by a padlock icon in the address bar) can suggest that the site lacks proper security measures. | http://www.example.com vs. https://www.example.com |
By familiarizing yourself with these characteristics, you can better protect yourself from inadvertently visiting harmful websites. Always exercise caution when clicking on links, especially those received via email or social media, and consider using tools that can help verify the safety of a URL before you visit it.
Secure Password Practices
In the realm of digital security, one of the foundational practices is the creation and management of robust passwords. This section delves into effective strategies to enhance your password security, ensuring that your personal data remains protected from unauthorized access.
A strong password is crucial as it serves as the first line of defense against intruders attempting to gain access to your accounts. Here are some essential tips to consider when setting up and maintaining your passwords:
- Complexity: Incorporate a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. This diversity makes it significantly harder for automated tools to guess your password.
- Length: Aim for a password length of at least 12 characters. Longer passwords provide a higher level of security as they exponentially increase the number of possible combinations.
- Uniqueness: Avoid using common words, phrases, or personal information that can be easily guessed or found through public records. Each account should have a unique password to prevent a domino effect if one account is compromised.
- Regular Updates: Periodically change your passwords, especially for sensitive accounts. This practice reduces the risk of your password being cracked over time.
- Password Managers: Consider using a reputable password manager to securely store and generate complex passwords. This tool can help manage multiple passwords without the need to remember them all.
Implementing these practices not only strengthens your security posture but also provides peace of mind knowing that your digital identity is well-protected. Remember, the effort put into creating and maintaining secure passwords is a small price to pay for the protection of your valuable information.
Secure Password Practices
In the realm of digital security, one of the foundational practices that significantly fortifies our defenses against unauthorized access is the implementation of robust password protocols. This section delves into the essential strategies for crafting and managing passwords that are not only strong but also resistant to common cyber attacks.
Crafting Strong Passwords
Creating a strong password involves several key elements. Firstly, it should be lengthy, ideally exceeding eight characters. Incorporating a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters enhances complexity, making it more difficult for attackers to crack. Avoid using easily guessable information such as birthdays, names of family members, or common words.
Regular Password Updates
Regularly updating your passwords is another crucial practice. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access even if a password has been compromised. It is recommended to change passwords every three to six months, especially for sensitive accounts like email and banking.
Unique Passwords for Each Account
Using a different password for each online account is vital. If a hacker gains access to one account and finds the same password used elsewhere, the impact can be widespread. Therefore, maintaining distinct passwords for different accounts significantly reduces the potential damage from a security breach.
Password Managers
For those who struggle to remember multiple complex passwords, password managers are an excellent solution. These tools securely store and manage your passwords, requiring you to remember only one master password. They also often include features like password generation and alerts for compromised or weak passwords.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Enabling two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. Even if an attacker guesses or obtains your password, they would still need access to your secondary authentication method, such as a text message code or an authentication app, to gain entry to your account. This significantly enhances the security of your digital profiles.
By adhering to these practices, individuals and organizations can greatly enhance their security posture, mitigating the risks associated with unauthorized access and data breaches.
Two-Factor Authentication Importance

In the realm of digital security, ensuring robust protection against unauthorized access is paramount. One of the most effective methods to enhance security is through the implementation of two-factor authentication (2FA). This section delves into the significance of 2FA and how it fortifies the defense against potential breaches.
Understanding Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two different authentication factors to verify their identity. This typically involves something you know (like a password), something you have (such as a mobile device), and sometimes something you are (biometrics). By adding this extra layer of security, the likelihood of unauthorized access is significantly reduced, even if the primary security measure, such as a password, is compromised.
The Benefits of Implementing 2FA
Implementing two-factor authentication offers several benefits. Firstly, it dramatically increases the security of user accounts. Even if a hacker manages to obtain a user’s password, they would still need the second factor to gain access. Secondly, it provides users with a sense of security, knowing that their accounts are less likely to be compromised. This is particularly important for sensitive accounts, such as banking or email, where the risk of fraud is high.
Integrating 2FA in Corporate Environments
In corporate settings, the adoption of two-factor authentication is crucial. It not only protects sensitive company data but also safeguards employee accounts. Companies should integrate 2FA into their IT policies and ensure that all employees are trained on its use. This includes understanding how to set up 2FA, how it works, and the importance of not sharing the second factor with others.
Challenges and Solutions
While two-factor authentication is highly beneficial, it does come with challenges. Users might find the process of entering a second factor inconvenient, especially if they are accustomed to quick logins. Additionally, there is the risk of losing the device that generates the second factor. To mitigate these challenges, companies can implement user-friendly 2FA methods, such as biometrics or push notifications, and educate users on backup options in case of device loss.
In conclusion, two-factor authentication is an essential tool in the fight against unauthorized access. By understanding its importance and implementing it effectively, both individuals and organizations can significantly enhance their digital security.
Educating Employees on Cybersecurity
In the realm of digital safety, fostering a culture of awareness and vigilance among staff members is paramount. This section delves into the strategies and methods necessary to equip employees with the knowledge to safeguard against various digital risks.
Key Components of Employee Cybersecurity Training
Effective training programs should cover a broad spectrum of topics, from understanding the mechanics of deceptive emails to recognizing the signs of data breaches. It is crucial that employees are taught to identify and respond appropriately to potential threats, thereby enhancing the overall security posture of the organization.
Role-Specific Training
Tailoring educational content to match the specific roles within an organization can significantly increase its effectiveness. For instance, those in managerial positions might require a deeper understanding of risk management and incident response, while administrative staff might focus more on basic security protocols and safe browsing practices.
Regular Updates and Refreshers
The digital landscape is ever-evolving, and so too must the educational materials. Regular updates to the training modules ensure that employees are aware of the latest tactics employed by cybercriminals. Refresher courses help in reinforcing the knowledge and keeping security practices top of mind.
Interactive Learning and Simulations
Incorporating interactive elements such as simulations and quizzes can make the learning process more engaging and effective. These tools not only test the employees’ understanding but also provide practical experience in dealing with real-world scenarios, enhancing their readiness to handle actual incidents.
By investing in comprehensive and ongoing cybersecurity education, organizations can empower their workforce to become a robust line of defense against digital threats. This proactive approach not only protects sensitive information but also contributes to a safer digital environment for all.
The Role of Antivirus Software
In the intricate landscape of digital security, antivirus software plays a pivotal role in safeguarding our electronic devices from various malicious activities. This section delves into how these protective tools function and their significance in maintaining a secure digital environment.
Antivirus software is designed to detect, thwart, and eradicate harmful programs that can compromise the integrity of your system. These programs are capable of identifying a wide array of threats, including viruses, worms, and Trojans, which can infiltrate your device through various means such as downloads, emails, or external devices. By continuously monitoring your system, antivirus software can prevent these malicious entities from executing and causing damage.
Moreover, modern antivirus solutions often include real-time scanning capabilities, ensuring that any new files or applications are checked immediately upon entry into the system. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of infection and helps in maintaining the overall health of your digital infrastructure.
Additionally, many antivirus programs offer features such as firewall protection, which adds an extra layer of security by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic. This dual functionality not only protects against external threats but also helps in preventing unauthorized access to your system.
In conclusion, the deployment of antivirus software is a critical component of any comprehensive security strategy. It not only defends against known threats but also plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating emerging risks in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Legal Protections Against Online Fraud
This section delves into the legal frameworks and measures designed to safeguard individuals and organizations from fraudulent activities conducted through digital channels. Understanding these protections is crucial for maintaining security and trust in electronic transactions.
In many jurisdictions, various laws and regulations have been established to combat fraudulent practices. Here are some key aspects of these legal protections:
- Consumer Protection Laws: These laws are designed to protect consumers from deceptive practices. They often include provisions that penalize businesses for misleading advertising or fraudulent transactions.
- Data Protection Regulations: Such regulations mandate how personal data should be handled. They impose strict rules on data collection, storage, and usage, aiming to prevent misuse of personal information.
- Cybercrime Laws: These laws specifically target crimes committed via the internet. They cover a wide range of offenses, including identity theft, hacking, and fraudulent use of electronic payment systems.
- Financial Fraud Laws: These laws are tailored to address fraudulent activities in the financial sector. They often include strict penalties for activities such as embezzlement, credit card fraud, and other financial deceptions.
- Civil Remedies: Victims of fraud can seek civil remedies, including compensation for losses incurred. Legal frameworks provide mechanisms for individuals to file lawsuits against perpetrators of fraudulent activities.
It is important for individuals and businesses to be aware of these legal protections and to utilize them effectively. Awareness and proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to fraudulent activities.
Furthermore, staying informed about updates to these laws and regulations is essential, as the legal landscape continually evolves to address new forms of fraud and cyber threats. Regular training and updates for employees and stakeholders can help ensure compliance and preparedness against fraudulent schemes.
Staying Updated on Latest Cyber Threats
In this section, we delve into the critical practice of keeping abreast of emerging digital risks. Staying informed is essential in the ever-evolving landscape of cyber dangers, helping individuals and organizations protect their digital assets effectively.
To maintain a robust defense against evolving digital risks, consider the following strategies:
- Regularly review security bulletins and updates from reputable cybersecurity sources.
- Subscribe to newsletters from cybersecurity experts and organizations to receive timely information on new threats.
- Attend webinars and workshops focused on cybersecurity trends and best practices.
- Join online forums and communities where cybersecurity issues are discussed, allowing for peer-to-peer learning and updates.
- Implement a policy of continuous learning within your organization, ensuring that all staff are aware of the latest digital risks and protective measures.
Additionally, it is crucial to:
- Monitor the effectiveness of current security measures and adjust them as necessary in response to new information about threats.
- Leverage technology tools that provide real-time threat intelligence to proactively safeguard against potential breaches.
- Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and address them promptly.
By adopting these practices, you can significantly enhance your readiness to confront and mitigate the impact of new cyber threats as they arise.
Remember, the key to effective cyber defense is not only in the tools and technologies you deploy but also in the knowledge and vigilance of those who use them.
For those who have just about any issues with regards to where by in addition to how you can make use of opt out white pages, you can call us at our own internet site.
